Gym Training The Ultimate Guide to Building Strength and Muscle
Starting a journey in gym training is one of the best decisions you can make for your long-term health. Whether your goal is to lose weight, build muscle, or simply improve your functional movement, a structured approach to the gym is essential. In this guide, we will explore the science and methodology behind effective training to ensure you get the best results possible.
Why Gym Training is Essential for Modern Fitness
In today’s sedentary world, our bodies often lack the physical stress needed to stay strong. Gym training provides a controlled environment where you can apply “progressive overload” to your muscles. This process forces your body to adapt, making you stronger, faster, and more resilient to injury. Beyond aesthetics, lifting weights improves bone density and metabolic rate.
Setting Your Goals for Gym Training
Before you pick up a dumbbell, you must define your objectives. Are you training for hypertrophy (muscle growth), raw strength, or endurance? Most beginners benefit from a balanced gym training program that incorporates compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. These exercises recruit multiple muscle groups and provide the highest return on investment for your time.
The Fundamental Principles of Muscle Growth
1. Progressive Overload
To see continuous progress in gym training, you must gradually increase the difficulty of your workouts. This can be done by adding more weight, increasing the number of repetitions, or decreasing rest time between sets. Without this, your muscles will plateau.
2. Proper Form and Technique
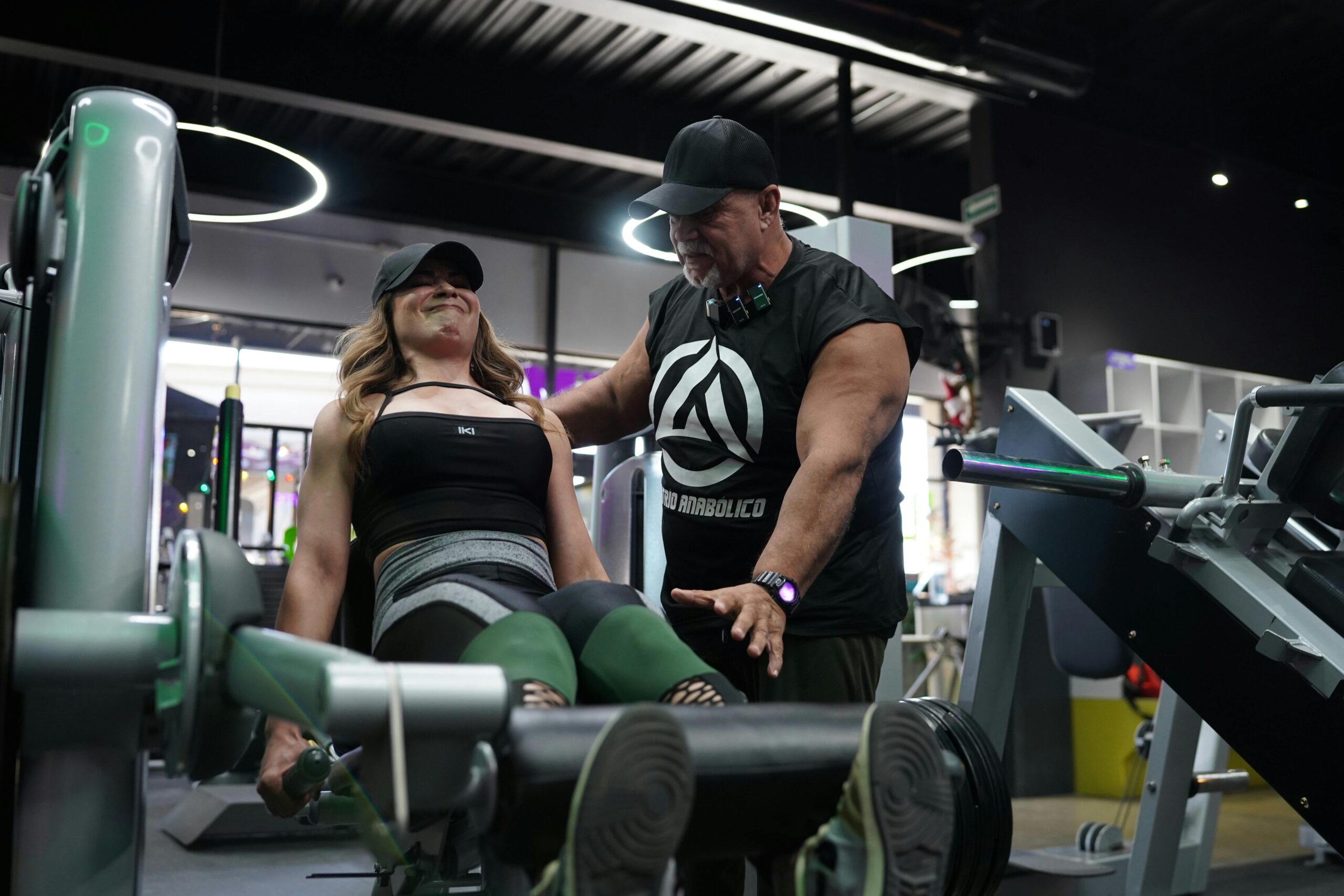
Lifting heavy is important, but lifting correctly is vital. Poor form leads to injuries that can sideline your progress for months. Always prioritize the quality of movement over the amount of weight on the bar.
3. Consistency and Recovery
Muscles don’t grow while you are in the gym; they grow while you sleep. A solid gym training routine must be paired with at least 7-9 hours of quality sleep and a high-protein diet to repair the micro-tears created during your workout.
Structuring Your Weekly Gym Routine
There are several ways to organize your week. Some prefer a “Full Body” split, while others enjoy a “Push/Pull/Legs” (PPL) split. The best routine is the one you can stick to consistently. If you can only commit to three days a week, a full-body gym training approach is usually the most effective way to hit every muscle group frequently enough to spark growth.
Nutrition: Fueling Your Gym Performance
You cannot out-train a bad diet. To support your gym training, focus on three main macronutrients:
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair (Chicken, eggs, lentils, whey).
- Carbohydrates: Your body’s primary fuel source for high-intensity lifting.
- Fats: Vital for hormone production and joint health.
Overcoming Plateaus and Staying Motivated
Everyone hits a wall eventually. If your progress stalls, try changing your rep ranges or introducing new exercises. Remember, gym training is a marathon, not a sprint. Celebrate small victories, like adding 2kg to your lift or feeling more energetic during the day.
Conclusion
Consistent is a lifestyle that pays dividends in every area of your life. It builds discipline, confidence, and a body that is capable of handling life’s challenges. Start slow, focus on form, and stay dedicated to the process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How many days a week should I do gym training?
A: For most people, 3 to 5 days per week is ideal. This allows enough frequency for growth while providing ample time for recovery.
Q: Can I lose weight through gym training alone?
A: While training burns calories and builds muscle (which boosts metabolism), weight loss is primarily driven by being in a calorie deficit through diet.






Leave feedback about this